Opiate addiction is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires professional help to overcome. Did you know that in the United States alone, opioid-involved overdose deaths rose from 68,630 in 2020 to 80,411 in 2021? These opiates are known to act as a depressant on the nervous system but became widely abused because of their euphoric and relaxing effects on their users.
If you or a loved one uses opiates, it’s important to be aware of opiate addiction warning signs and seek professional help to prevent worsening conditions.
Understanding Opiate Addiction
Opiates are a class of drugs derived from the opium poppy plant, which are prescribed by physicians or psychiatrists to work as a depressant on the nervous system, while some are prescribed in order to assist in lessening emotional distress and help individuals fall asleep.
You’ve probably heard of some prescribed opiates like Vicodin, codeine, morphine, OxyContin, and Percocet. These are known to provide relief from intense and/or chronic pain. However, these substances have been widely known to cause addiction among their users for eliciting feelings of euphoria and intense relaxation. Continued usage can alter the brain’s chemistry and reward system, making it hard for users to stop using, even if they try to stop.
Causes and Risk Factors of Opiate Addiction
The causes of opiate addiction are varied and can be attributed to different factors. These include the following:
- Genetics: Research has demonstrated a strong genetic link between substance abuse and addiction, including opiate addiction. People with a family history of substance abuse are more likely to develop an addiction than those without any history.
- Environment: A person’s environment can also play a significant role in their likelihood to experiment with and abuse opioids. Exposure to drug use, chronic stress, or emotional turmoil can drive individuals to seek relief through the use of opiates.
- Risk factors: Other factors that increase the risk of opiate addiction include chronic pain conditions, pre-existing mental health issues, peer pressure, easy access to opiates, poor interpersonal relationships, exposure to crime or violence, experiences of abuse or neglect, and lack of parental involvement.
Co-Occurring Disorders of Opiate Addiction
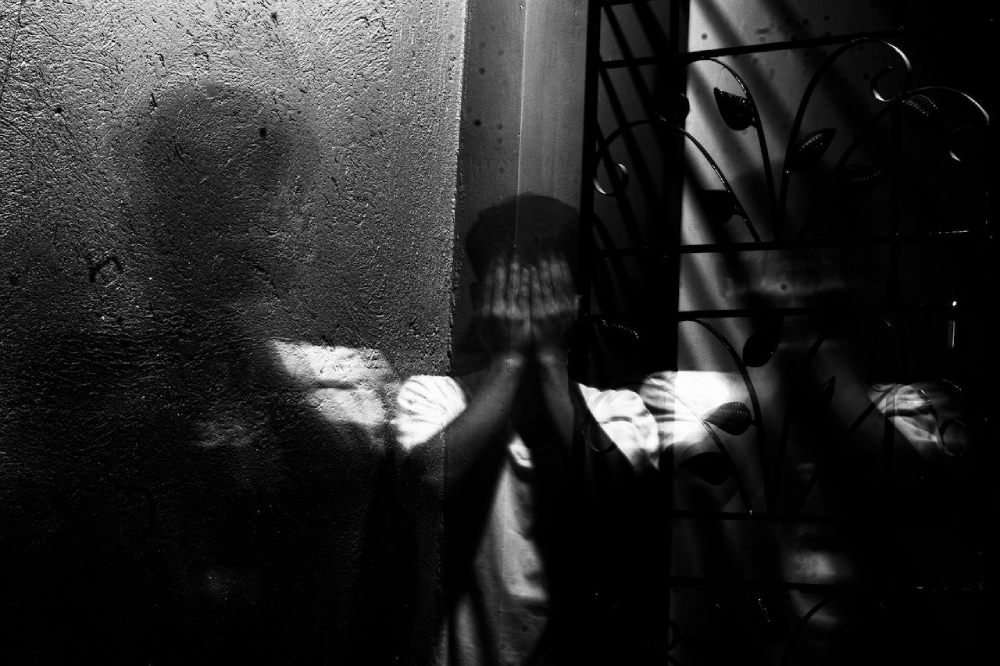

Many individuals who struggle with opiate addiction also have co-occurring mental health disorders. These may include depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), bipolar disorder, or borderline personality disorder. These conditions can make it even more challenging to overcome addiction and may require specialized treatment.
Warning Signs and Symptoms of Opiate Addiction
- Physical symptoms
Someone struggling with opiate addiction might experience physical symptoms like constricted pupils, frequent nausea and sleep disturbances, changes in eating patterns that can result in constipation or diarrhea, and a slowed heart rate and breathing.
You should also check for track marks or scars on their arms or other areas of their body, as these are signs that they may be injecting drugs frequently. - Behavioral changes
If you notice a loved one experiencing changes in behavior, like constantly borrowing or stealing money from others, becoming increasingly secretive, slurred speech, having sudden and unprovoked anger outbursts, withdrawing from social activities, and neglecting responsibilities at home or work, then they may be struggling with opiate addiction. - Psychological symptoms
Someone might also be struggling with opiate addiction if they begin to experience some psychological symptoms like mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and depression. They are also constantly agitated or restless. - Changes in their social circles
A loved one may begin to distance themselves from friends and family members who don’t use drugs and may start to spend more time with individuals who share their addiction. - Increased tolerance and withdrawal symptoms
Over time, an individual may develop a tolerance to opiates, and they would need more of the drug to achieve the same effects. When they stop using, they may experience withdrawal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, muscle aches, and insomnia.
Dealing With Opiate Addiction Warning Signs
If you suspect a loved one is struggling with opiate addiction, or you are experiencing these symptoms yourself, it’s important to approach the situation with compassion and understanding. Encourage them to seek professional help and offer to support them throughout the recovery process.
At Altitude Recovery, we understand how sensitive a situation can be when it comes to seeking professional help for drug addiction, which is why we take a personalized approach for every individual and we always support our patients on their road to recovery.
If you or a loved one is ready to receive treatment, don’t hesitate to contact us today and we’ll assist you.